Difference between revisions of "Git"
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
* '''g''' Goto nth revision | * '''g''' Goto nth revision | ||
* '''q''' Exit the time machine. | * '''q''' Exit the time machine. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= See also = | = See also = | ||
Revision as of 14:21, 21 September 2016
Packages to interfere with the git version control system.
Full interfaces
Magit
Magit is a great Emacs mode for working with Git repositories. It provides a convenient interface for the most common Git operations. Please visit its own Magit page.
Specific use cases
Git blame
Git-blame is a package, available in ELPA, which provides a minor mode for incremental blame.
Show last commit message for current line
This package provides a function called git-messenger:popup-message that when called will pop-up the last git commit message for the current line. This uses the git-blame tool internally.
Available in ELPA.
Highlight uncommited changes
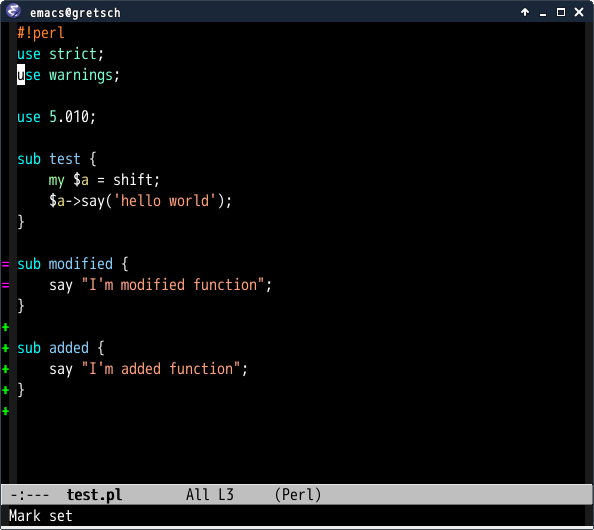
Git gutter
Git-gutter is an extension to highlight uncommitted changes on the left side of the window, indicating wether a line has been inserted, modified or deleted, and allowing you to jump between and revert them selectively. diff-hl does it too and works with Git, Mercurial, Bazaar and Svn, and it provides similar functionnality for dired. Both are available in ELPA. They are Tramp-aware.
After installation, call the minor modes or enable them:
(add-hook 'python-mode-hook 'git-gutter-mode)
Jump between changes
To jump between changes: M-x git-gutter:next-hunk or M-x diff-hl-next-hunk.
Highlight diffs
Diff-hl goes a little further than git-gutter in that it can highlight the uncommited diffs, even from Dired. And we can get them on the fly while we type:
(diff-hl-flydiff-mode)
Browse and stage hunks with Helm
Helm-hunks allows to jump around git hunks with helm, to preview them on the fly, and to stage them.
Commit on every change
git-auto-commit-mode (on MELPA) is a minor mode that tries to commit a change to a file after every save. It can also push automatically.
See previous versions of file
It's very easy with git-timemachine. Once you have called M-x git-timemachine you'll have the keys:
- p Visit previous historic version
- n Visit next historic version
- w Copy the abbreviated hash of the current historic version
- W Copy the full hash of the current historic version
- g Goto nth revision
- q Exit the time machine.
See also
See also the full list of packages to interact with Github, Gitlab and others in the Github page.
Install every package at once
See a full list and a method to install them all at once on tarsiu's github page.