Difference between revisions of "Dired"
(→View image thumbnails: add new DISS, image slideshow) |
(→See Also: add filetree) |
||
| Line 204: | Line 204: | ||
With ranger (formerly known as evil-ranger, even if it wasn't specific to evil-mode), we have most of ranger's functionalities in Dired: 3 panes layout, previews, etc. Very nice ! | With ranger (formerly known as evil-ranger, even if it wasn't specific to evil-mode), we have most of ranger's functionalities in Dired: 3 panes layout, previews, etc. Very nice ! | ||
| + | |||
| + | === [https://github.com/knpatel401/filetree file-tree] - display and operate and a file list as a tree === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ```file-tree``` offers two things: it's a file tree viewer, and it allows to write and display ```notes``` associated to files. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It offers actions similar to Dired: mark files and take actions (copy, delete, rename…). | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can find a demo video on Youtube here: https://youtu.be/-KrMaLq8Bms | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[[File:Evil-ranger-preview.png|800px]] | [[File:Evil-ranger-preview.png|800px]] | ||
Revision as of 13:09, 5 November 2021
| Description | File Manager for Emacs. |
|---|---|
| Author | Sebastian Kremer |
| Maintainer | FSF |
| Source | http://git.savannah.gnu.org/cgit/emacs.git/tree/lisp/dired.el |
| Part of Emacs | yes |
Dired is a inbuilt File Manager for Emacs. Its arguably the best file manager with the functionality it possesses. Unlike any other file managers the directory listing is just as an another buffer of Emacs with dired-mode as Major Mode.
Usage
Dired has countless functionality. The best way to learn it is to try it out. Open a dired buffer and look at the commands listed in the menus.
- [C-x d] (or M-x dired)
- ask for a directory and puts you into a buffer with direct listing of that directory.
- [C-x C-j] (or M-x dired-jump)
- jump to a dired buffer corresponding to the current buffer (This require loading Dired Extra).
In the minibuffer, while doing 'Find File':
- [C-d]
- jump to a dired buffer corresponding to the directory in the minibuffer.
Basic commands
- [ RET]
- Open the file/Directory. You can use a to open the directory without creating another buffer.
- [ q]
- Close the dir
- [ i]
- i: open directory in subtree. Use ^ to go up one level. With a prefix argument (C-u i), you can edit the ls switches used for the listing. So you can add R to expand the whole tree starting at this subdirectory.
- [C]
- Copy file
If you set (setq dired-dwim-target t), split your window and open another dired buffer on the other window, Dired will suggest it as the default target directory for the copy and rename commands.
- [R]
- Rename file
- [D]
- Delete file
- [+]
- create a new dir
Mark/unmark files
[m]
- mark a file
[u]
- unmark a file
[U]
- unmark all marked
[%m]
- mark by pattern
Edit filenames and permissions
Wdired mode (writable dired) allows you to enter a mode where you can edit filenames, symbolic link target and filenames permissions as you would in a regular buffer. It is particularly great to do some editing based on search and replace.
[C-x C-q]
- enter wdired mode (calls wdired-change-to-wdired-mode). Type C-c C-c to validate your changes or C-c ESC to abort.
M-x customize-group RET wdired to customize wdired behavior.
Note: in Dired, you can rename a single file or move the marked ones with R.
Sort files
By default, typing s will toggle sorting by date. You can change the listing switches (of GNU ls) with C-u s.
You can customize the variable dired-listing-switches. For example,
(setq dired-listing-switches "-aBhl --group-directories-first")
will display directories first. You can then customize per-directory local variables.
Dired+ (see below) offers more options (sort by size, by extension,…) and will add a menu entry.
Find files recursively
find-name-dired
With M-x find-name-dired, you'll be asked for the base directory, a file wildcard and the matching files will be displayed in a Dired buffer. It uses the find GNU utility.
Similar commands are find-grep-dired or find-dired. More information can be read in the documentation.
Interactive selection with Projectile
Projectile, coupled with M-x helm-projectile, lets you find recursively and interactively files in your project. This command does not use a Dired buffer.
View image thumbnails (image-dired)
Viewing images is a builtin feature of Dired (press Enter or v on an image file). On Emacs24.4, pressing n and p will show the next or previous image file. But if you want to navigate between image thumbnails, use the (builtin too) image-dired. You can directly call it with M-x image-dired, or mark the images you want to look at in the dired buffer (with m) and then type C-t d (image-dired-display-thumbs).
Tag images
More advanced features include image tags, which are metadata used to categorize image files. The tags are stored in a plain text file configured by image-dired-db-file.
To tag image files, mark them in the dired buffer and type C-t t (image-dired-tag-files). This reads the tag name in the minibuffer.
To mark files having a certain tag, type C-t f (image-dired-mark-tagged-files). After marking image files with a certain tag, you can use C-t d to view them.
You can also tag a file directly from the thumbnail buffer by typing t t and you can remove a tag by typing t r.
There is also a special “tag” called “comment” for each file (it is not a tag in the exact same sense as the other tags, it is handled slightly different). That is used to enter a comment or description about the image. You comment a file from the thumbnail buffer by typing c. You will be prompted for a comment. Type C-t c to add a comment from Dired (image-dired-dired-comment-files).
Rotate images
Image-Dired also provides simple image manipulation. In the thumbnail buffer, type L to rotate the original image 90 degrees anti clockwise, and R to rotate it 90 degrees clockwise. This rotation is lossless, and uses an external utility called JpegTRAN.
See also: Dired Image SlideShow (DISS)
DISS is an external package, published in 2021, that builds on Dired and Image-mode to provide a mode to browse images and view them in a slideshow.
Diss features include:
- Use any Dired buffer (including find-dired) as the source of images.
- Manual navigation, or automatic advance with delay.
- Easily categorize files: mark, flag for deletion, or apply an arbitrary marker character directly from the image.
- Advancing images can optionally apply a marker to every image.
- Infinite loop, or pop back to image list when finished.
- Multiple slideshow configurations can be named and saved.
- Quick image tools: Rotate CW/CCW, smart fit, fit height, fit width, rename.
It can also work with the lightweight Feh image viewer.
See Also
Dired+ - a package that extends the functionalities of Dired
Direx - a general purpose directory/tree explorer
Dired-du - display recursive directory sizes
Dired-du (in GNU ELPA) defines a minor mode dired-du-mode to show
the recursive size of directories in Dired buffers.
If the du program is available, then the directory sizes are
obtained with it. Otherwise, the directory sizes are obtained
with Lisp. The former is faster and provide a more precise value.
For directories where the user doesn't have read permission,
the recursive size is not obtained.
Once this mode is enabled, every new Dired buffer displays
recursive dir sizes.
To enable the mode at start up add the following into your Init File:
(add-hook 'dired-mode-hook #'dired-du-mode)
but beware that it can take a long time.
So you can also enable this mode once in a buffer: M-x dired-du-mode, and disable it when you're done.
You can also select files (with the selector * for example) and call M-x dired-du-count-sizes, to count the number of marked files and how much space they use.
Dired-details - a library to make file details hide-able
dired-open - open files with external applications
Many times, you want to open media files, pdfs or other documents with an external application. There's remedy for that too, namely dired-guess-shell-alist-user, but that is still not as convenient as just hitting enter.
dired-open is part of dired-hacks (in MELPA).
This feature is also the goal of openwith (in MELPA).
Dired-k - add colored icons depending on the git status
See here: http://wikemacs.org/wiki/Git#Colorize_Dired_output_depending_on_the_file_git_status
dired-subtree - insert the subdirectory (with the i key) directly below its line
Treemacs, a tree-style file explorer
see Treemacs. It has optional git integration (showing the status of files with different faces), optional follow-mode, projectile integration (quickly open treemacs at any known project’s root directory), session persistence with desktop-save-mode, and more.
dirtree - a directory tree view panel
peep-dired - file previews à la ranger
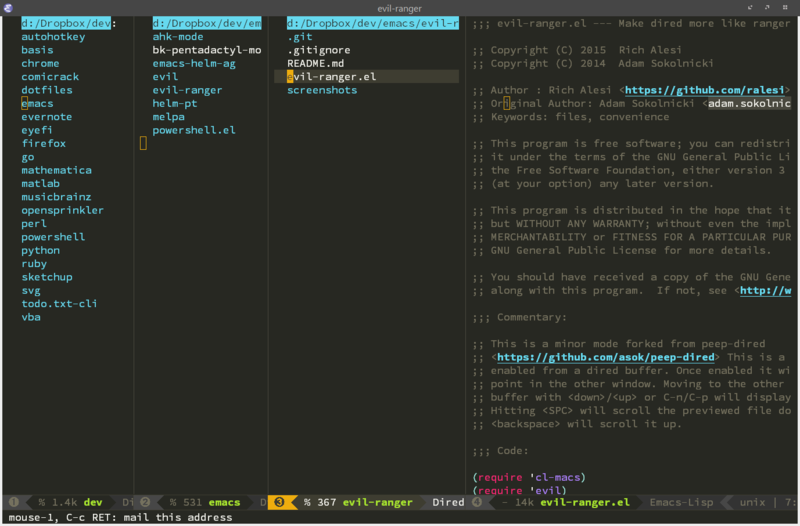
Ranger is a file browser for the terminal that has a nice navigation system composed of three panes: the current directory at the middle, the previous one to the left, and a preview of the file the cursor is on to the right. Peep-dired mimics a handy two-panes navigation with instant preview.
Ranger- Ranger functionalities in Dired
With ranger (formerly known as evil-ranger, even if it wasn't specific to evil-mode), we have most of ranger's functionalities in Dired: 3 panes layout, previews, etc. Very nice !
file-tree - display and operate and a file list as a tree
```file-tree``` offers two things: it's a file tree viewer, and it allows to write and display ```notes``` associated to files.
It offers actions similar to Dired: mark files and take actions (copy, delete, rename…).
You can find a demo video on Youtube here: https://youtu.be/-KrMaLq8Bms